| [1]Klisic PJ. Congenital dislocation of the hip-amisleading term: Brief report. Bone Joint Surg.1991;71(1):136.
[2]Gem M, Arslan H, Ozkul E, et al.One-stage bilateral open reduction using the anterior iliofemoral approach in developmental dysplasia of the hip. Acta Orthop elg. 2014; 80(2):211-215.
[3]Desteli EE, Pi?kin A, Gülman AB, et al.Estrogen receptors in hip joint capsule and ligamentum capitis femoris of babies with developmental dysplasia of the hip. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc.2013;47(3):158-161.
[4]Zhang L, Yu LD, Yang GJ.Soft tissue balancing in the total hip arthroplasty for severe developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi.2008;46 (17):1299-1302.
[5]Ooishi T.Experimental study on the etiology of pathogenesis of acetabulardysplasia in congenital dislocation of the hip.Nippon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi.1990;64(10):958-975.
[6]毛宾尧.髋关节外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1998:331-353.
[7]姜俊,麻宏伟,戴晓梅.先天性髋关节脱位的遗传流行病学研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2006,35(5):514-517.
[8]Price KR, Dove R, Hunter JB.The use of X-ray at 5 months in a selective screening programme for developmental dysplasia of the hip.J Child Orthop.2011;5(3):195-200.
[9]Ömero?lu H, Inan U.Inherited thrombophilia may be a causative factor for osteonecrosis of femoral head in male patients withdevelopmental dysplasia of the hip: a case series. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2012;132(9):1281-1285.
[10]Wang E, Liu T, Li J,et al.Does swaddling influence developmental dysplasia of the hip?: An experimental study of the traditional straight-leg swaddling model in neonatal rats.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(12):1071-1077.
[11]Bachy M, Thevenin-Lemoine C, Rogier A, et al.Utility of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) after closed reduction of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Child Orthop. 2012;6 (1): 13-20.
[12]Xu M, Gao S, Sun J, Yang Y, et al. Predictive values for the severity of avascular necrosis from the initial evaluation in closed reduction ofdevelopmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2013;22(3):179-183.
[13]Lee CB, Mata-Fink A, Millis MB, et al.Demographic differences in adolescent-diagnosed and adult-diagnosed acetabular dysplasia compared with infantile developmental dysplasia of the hip.J Pediatr Orthop.2013;33(2):107-111.
[14]Rosendahl K, Tomà P.Reply to Riccabona et al. regarding screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip. Pediatr Radiol.2013;43(5):641-642.
[15]Cook SD, Wolfe MW, Salkeld SL, et al.Effect of recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 on healing of segmental defects in non-human primate. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1995;77(5): 734.
[16]Hidaka C, Goshi K, Rawlins B,et al.Enhancement of spine fusion using combined gene therapy and tissue engineering BMP-7 expressing bone marrow cells and allograft bone. Spine.2003;28(18): 2049.
[17]Xu M, Gao S, Sun J, et al. Predictive values for the severity of avascular necrosis from the initial evaluation in closed reduction of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop B.2013;22 (3):179-183.
[18]Tréguier C, Baud C, Ferry M, et al. Irreducible developmental dysplasia of the hip due to acetabular roof cartilage hypertrophy. Diagnostic sonography in 15 hips.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2011;97 (6):629-633.
[19]Azzopardi T, Van Essen P, Cundy PJ, et al. Late diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip: an analysis of risk factors. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2011;20(1):1-7.
[20]Sharpe P, Mulpuri K, Chan A, et al.Differences in risk factors between early and late diagnosed developmental dysplasia of the hip. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2006;91(3): F158-162.
[21]Shorter D, Hong T, Osborn DA. Screening programmes for developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborn infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;7(9): CD004595.
[22]Ewald E, Kiesel E.Screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborns.Am Fam Physician. 2013;87(1):10-11.
[23]Roposch A, Ridout D, Protopapa E,et al.Osteonecrosis complicating developmental dysplasia of the hip compromises subsequent acetabular remodeling. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(7):2318-2326.
[24]Mahan ST, Katz JN, Kim YJ.To screen or not to screen? A decision analysis of the utility of screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(7): 1705-1719.
[25]Rális Z, McKibbin B. Changes in shape of the human hip joint during its development and their relation to its stability.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1973;55(4):780-785.
[26]Reddi AH, Anderson WA.Collagenous bone matrix induced endochondral ossification and hemopoiesis. J Cell Biol. 2006; 69:557-572.
[27]Sionek A, Czubak J, Kornacka M, et al.Evaluation of risk factors in developmental dysplasia of the hip in children from multiple pregnancies: results of hip ultrasonography using Graf's method. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2008;10(2): 115-130.
[28]Yang G, Zhu Z, Wang Y, et al.Bone Morphogenetic Protein-7 inhibits ilica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats.Toxicol Lett. 2013;29:S0378-4274.
[29]Odabas S, Feichtinger GA, Korkusuz P, et al. Auricular cartilage repair using cryogel scaffolds loaded with BMP-7-expressing primary chondrocytes. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012, 26. doi: 10.1002/term.1634
[30]Kim HK, Kim JH, Park DS, et.al.Osteogenesis induced by a bone forming peptide from the prodomain region of BMP-7, Biomaterials. 2012; 33(29):7057-7063.
[31]Soran N, Altindag O, Aksoy N,et al.The association of serum prolidase activity with developmental dysplasia of the hip. Rheumatol Int. 2013;33(8):1939-1942. |
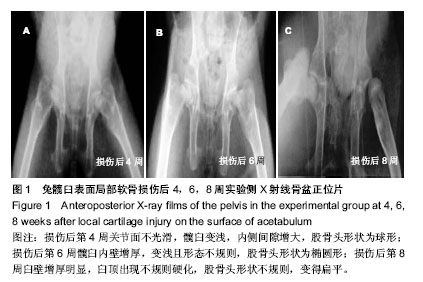
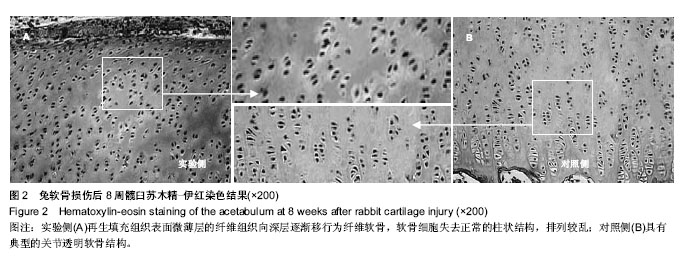
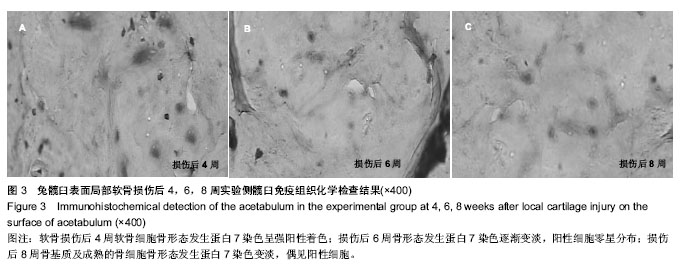
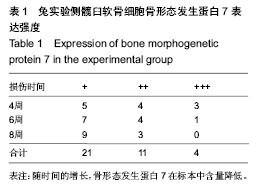
.jpg)